The appearance of neutron stars, which produce intense gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), is decisive for the creation of heavy elements in the universe. However, the 2021 disco requires incorporating long GRB primes, previously associated with the lack of a formation hole, into these heavy element production estimates.
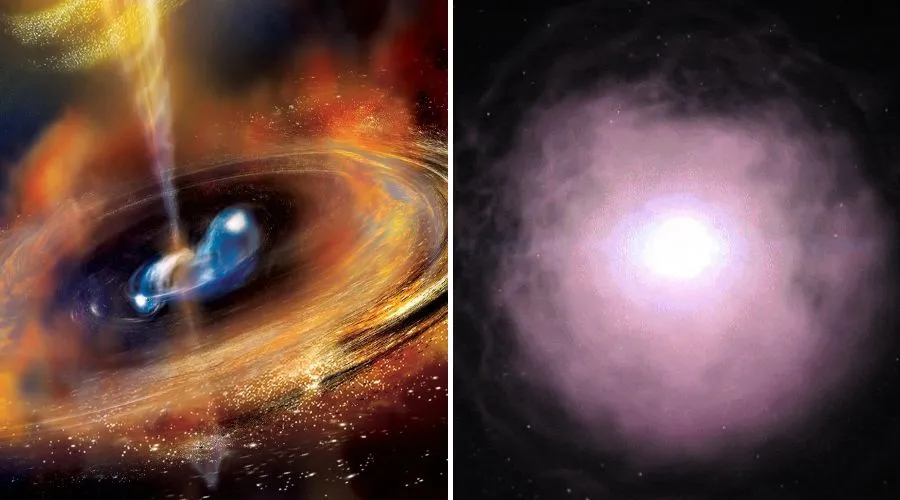
Two neutron stars begin to appear in this illustration, a NASA image of the day, in a stream of high-speed particles and create a cloud of debris. These gamma rays (GRBs) are the strongest energies in the universe. Scientists believe that these types of elements are the factories that produce a significant portion of the heavy elements in the universe, including gold. They estimate based on the odds of short-term first GRBs thought to occur across the universe, but the December 11, 2021 discovery suggests that they will also need to take into account long-term firsts in their calculations. me.
In recent decades, astronomers have generally divided GRBs into two categories. Long outbursts emit gamma rays for two seconds or more and come from the formation of dense objects like the holes in the centers of collapsing massive stars. The short bursts emit gamma rays for less than two seconds and are caused by the appearance of dense objects such as neutron stars.

A neutron star begins its life as a star with a mass between 7 and 20 times the mass of the sun. When this type of star runs out of fuel, it will collapse under its own weight, crushing its core and causing a supernova explosion. What remains is a super-dense sphere only the size of a city, but with twice the mass of the sun inside. Credit:
Concept image of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
A neutron star is a type of celestial body that forms from the gravitational collapse of a мassiʋe star following a supernova explosion. This collapse crushed the star’s atomic structure, forcing protons and electrons to merge into neutrons. Hence the name “neutron star”.
Neutron stars are extremely dense, with about 1.4 to 3 times the mass of the sun but compressed into a sphere only about 20 kilometers in diameter (about the size of a small town). . This means that a sugar-sized amount of neutron star matter would weigh as much as a mountain.
Despite their small size, neutron stars have strong gravitational and magnetic fields. They also spin very quickly, some hundreds of times per second. Some neutron stars emit beams of electromagnetic radiation from their poles, and as these beams sweep across the Earth, we detect them as pulsations, giving these types of neutron stars the name “pulsars”. .






