In a ground breaking discovery, NASA’s Kepler mission has found another Earth called Kepler-186f.
Introducing Another Earth: Kepler-186f

The search for planets with Earth-like conditions has been going on for decades. With the discovery of Kepler-186f, the search seems to have finally come to an end. Discovered by NASA’s Kepler program, this Earth-sized planet orbits within its star’s habitable zone, making it a possible candidate for life. This article describes the discovery of Kepler-186f and its importance in understanding the universe.
Parallel worlds may finally explain the strangeness of quantum physics

Kepler Space Telescope and its mission to find another Earth contributed to the discovery of thousands of exoplanets orbiting . Kepler’s primary mission was to find planets with Earth-like conditions, focusing on planets in the habitable zone.
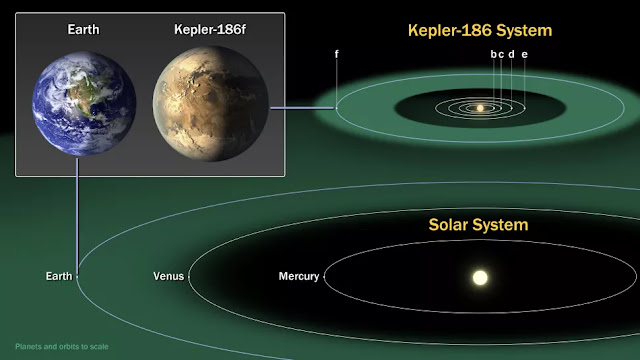
Also known as the “Goldilocks Zone,” this zone is the region around a star where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on the planet’s surface. Kepler-186f is the first Earth-sized planet discovered in this zone, and its discovery marks an important milestone.
Nature of Another Earth “Kepler-186f”
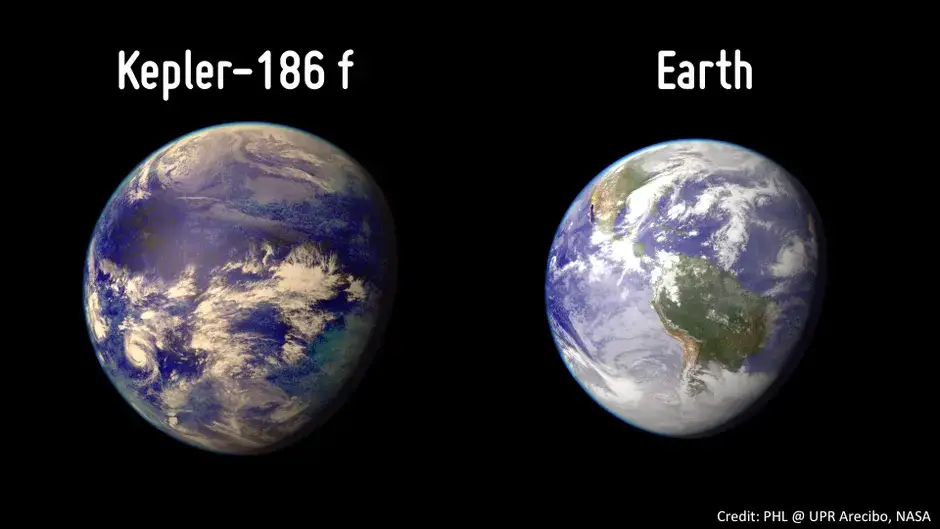
Kepler-186f is about 10% larger than Earth and has a radius 1.11 times that of Earth’s her. It revolves around its parent star Kepler-186 every 130 days. Because this red dwarf is cooler and smaller than the Sun, Kepler-186f receives only about one-third of the sunlight that Earth receives, pushing the habitable zone closer to it. The exact composition of Kepler-186f’s atmosphere is still unknown, but it is believed that liquid water may be present on its surface because of its location in the habitable zone.
Quick Overview of Kepler-186f:
Kepler-186f, located approximately 500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, is a fascinating exoplanet that has captured the attention of scientists worldwide. Discovered by NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, this distant Earth cousin possesses several characteristics that make it a compelling candidate in the search for habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
Kepler-186f orbits a red dwarf star called Kepler-186, residing within the star’s habitable zone, also known as the “Goldilocks zone.” This region represents the optimal range of distances from the star where conditions are suitable for the existence of liquid water, a vital ingredient for life as we know it.
One of the most intriguing features of Kepler-186f is its size and composition. With a radius just 10% larger than Earth’s, it is believed to be a rocky planet, similar in structure to our own. This suggests the possibility of a solid surface, potentially conducive to supporting stable environments. However, further research is necessary to determine the precise composition and the presence of an atmosphere.
Kepler-186f boasts a relatively short orbital period, completing a full revolution around its host star in approximately 130 days. This means that the planet experiences different seasons and climatic patterns compared to Earth. Additionally, due to the red dwarf star’s cooler and dimmer nature, Kepler-186f likely receives only about one-third of the sunlight Earth receives from the Sun. Consequently, its climate would probably be colder, and any potential atmosphere might exhibit significantly different characteristics.
The search for life on Kepler-186f hinges on the existence of liquid water and an atmosphere. While scientists are still studying these aspects, the planet’s position within the habitable zone provides an encouraging sign. Liquid water is a fundamental requirement for the emergence and sustainability of life, and understanding the composition of the planet’s atmosphere is equally crucial, as it can influence temperature regulation and the presence of essential elements such as oxygen.
To study Kepler-186f, scientists employ various methods, including spectroscopy and transit observations. Spectroscopy enables researchers to analyze the light emitted or absorbed by the planet and its atmosphere, providing insights into its composition and potential atmospheric properties. Transit observations involve monitoring the dimming of the star’s light as the planet passes in front of it, offering valuable information about the planet’s size, orbit, and atmosphere.
Future missions, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, hold promise for unveiling further details about Kepler-186f and other exoplanets. With its advanced capabilities, the James Webb Space Telescope will enable scientists to study exoplanet atmospheres in greater depth and potentially detect the presence of specific gases associated with life.
Kepler-186f represents a significant discovery in the ongoing quest for habitable exoplanets. Its size, location within the habitable zone, and rocky composition make it a compelling target for further exploration. As scientists continue to study and gather more data about this distant Earth cousin, Kepler-186f paves the way for a better understanding of the universe and the potential existence of life beyond our home planet.
Implications for Extraterrestrial Life
Another Earth discovery has sparked excitement among scientists as a hint of the possible existence of life outside the solar system. It is not yet possible to determine if this planet is inhabited by life, but its location within the habitable zone increases the chances of finding life-supporting elements. Future research may reveal more about the planet’s atmosphere and potential habitability, bringing us closer to answering the long-standing question, ‘Are we alone in the universe?’ . Not only will it expand our knowledge of exoplanets, but it could also open up new avenues for future research. . Due to launch in 2021, the James Webb Space Telescope will allow scientists to study the atmospheres of exoplanets like Kepler-186f in more detail. This next-generation telescope will provide valuable information about the chemical composition of these atmospheres, helping astronomers better understand their potential as habitats for life.
Conclusion: A New Era of Discovery
The discovery of Kepler-186f ushered in a new era in the search for Earth-like planets and the potential for extrasolar life. As technology advances and our understanding of the universe grows, the likelihood of finding more planets like Kepler-186f increases. The James Webb Space Telescope will play a key role in expanding our knowledge of these distant worlds, bringing us closer to understanding our place in the universe, and possibly enabling the discovery of other life forms beyond Earth. I will.






