A new algorithm developed by Chinese company Baidu Research is dramatically faster than prior methods and shown to boost the antibody response of mRNA vaccines by up to 128 times.

Baidu Research is the research arm of Baidu, one of the largest technology companies in China. Established in 2014, it has since then been involved in various research activities such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, computer vision, robotics, and other areas of artificial intelligence.
This week, scientists from Baidu Research have announced an AI algorithm that can rapidly design highly stable COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sequences that were previously unattainable. The algorithm, named LinearDesign, represents a major leap in both stability and efficacy for vaccine sequences, achieving a 128-fold increase in the COVID-19 vaccine’s antibody response.
“This research can apply mRNA medicine encoding to a wider range of therapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies and anti-cancer drugs, promising broad applications and far-reaching impact,” said Dr. He Zhang, Staff Software Engineer at Baidu Research.
His team collaborated with Oregon State University, StemiRNA Therapeutics, and the University of Rochester Medical Center, to publish a study in the prestigious journal Nature, through Accelerated Article Preview (AAP). This marks the first time a Chinese tech company has been credited as the first affiliation on a paper published in Nature.
mRNA, or messenger RNA, has emerged as a revolutionary technology for vaccine development and potential treatments against cancer and other diseases. Carrying genetic instructions from DNA to a cell’s protein-making machinery, it enables the creation of specific proteins for various functions in the human body. With numerous advantages in safety, efficacy, and production, mRNA has been swiftly adopted for COVID-19 vaccine development.
However, mRNA has a natural instability, which leads to insufficient protein expression that weakens a vaccine’s capacity to stimulate strong immune responses. This also poses challenges for storing and transporting mRNA vaccines, especially in developing countries where resources are often limited.
In their paper, Dr. He Zhang and colleagues explain how this complex biological problem can be tackled using NLP. Although NLP and biology may at first glance appear unrelated, the two fields share strong mathematical connections. In human language, a sentence consists of a word sequence and an underlying syntactic tree with noun and verb phrases, which together convey meaning. Likewise, an RNA strand has a nucleotide sequence and an associated secondary structure based on its folding pattern.
The researchers used a technique in language processing called “lattice parsing”, which represents potential word connections in a lattice graph and selects the most plausible option based on grammar. Similarly, they created a graph to compactly represent all mRNA candidates, using deterministic finite-state automaton (DFA). Applying lattice parsing to mRNA, finding the optimal mRNA is akin to identifying the most likely sentence among a range of similar-sounding alternatives.
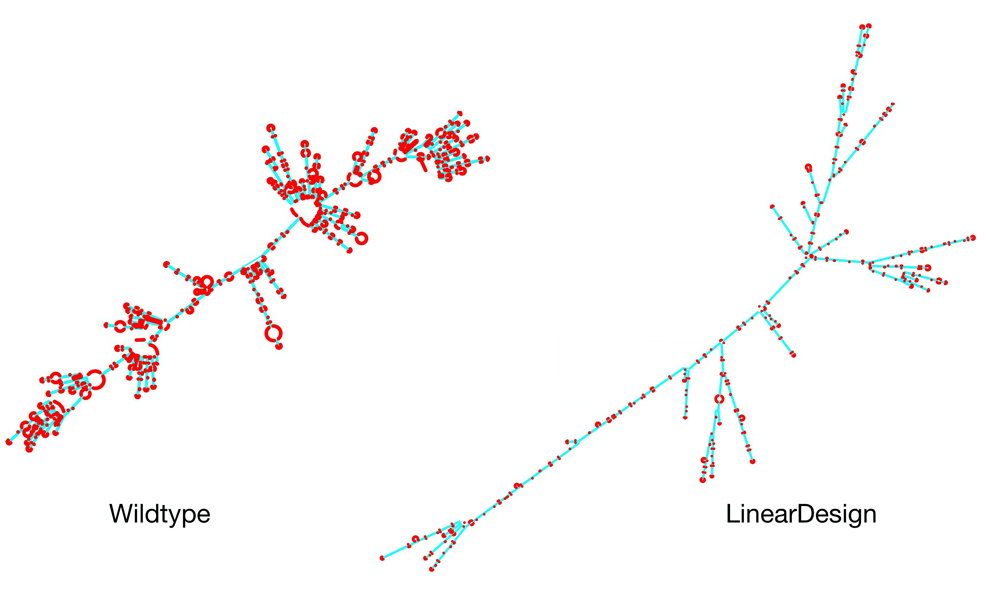
Using this approach, LinearDesign takes a mere 11 minutes to generate the most stable mRNA sequence to encode a spike protein. Without this algorithm, enumerating all possible COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sequences would take 10616 billion years. There are approximately 10632 mRNAs that can be translated into the same SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, presenting insurmountable challenges for prior methods.
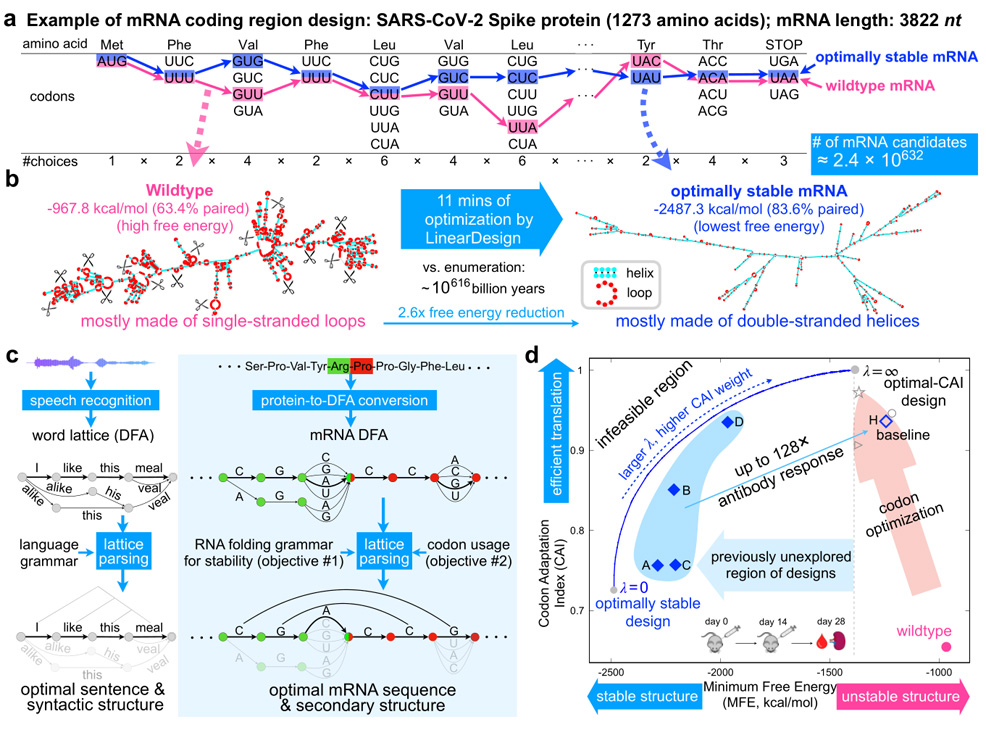
In head-to-head comparisons, LinearDesign demonstrated substantially improved results compared to existing vaccine sequences. The COVID-19 mRNA had a five-fold increase in stability (mRNA half-life), a three-fold increase in protein expression, and an incredible 128-fold increase in antibody response.
For varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine sequences, the study reported up to a six-fold increase in mRNA stability, a 5.3-fold increase in protein expression levels and an eight-fold increase in antibody response.
As illustrated below, a “wildtype” RNA sequence contains numerous unpaired nucleotide loops, which leads to less stability. The LinearDesign algorithm can generate sequences with significantly fewer loops, for a more stable structure.
“The vaccines designed through our method may offer better protection with the same dosage, and potentially provide equal protection with a smaller dose, leading to fewer side effects,” Dr. Zhang explained. “This will greatly reduce the vaccine research and development costs for biopharmaceutical companies while improving the outcomes.”
Baidu has already begun a partnership with French biotech company Sanofi, to integrate the new LinearDesign algorithm into Sanofi’s product design pipeline for mRNA vaccine and drug development.