Saturn’s sixth-largest moon, Enceladus has all the right ingredients for life. This revelation, based on a new analysis of NASA’s Cassini space mission data, suggests that other similar moons in the outer solar system could also be habitable.
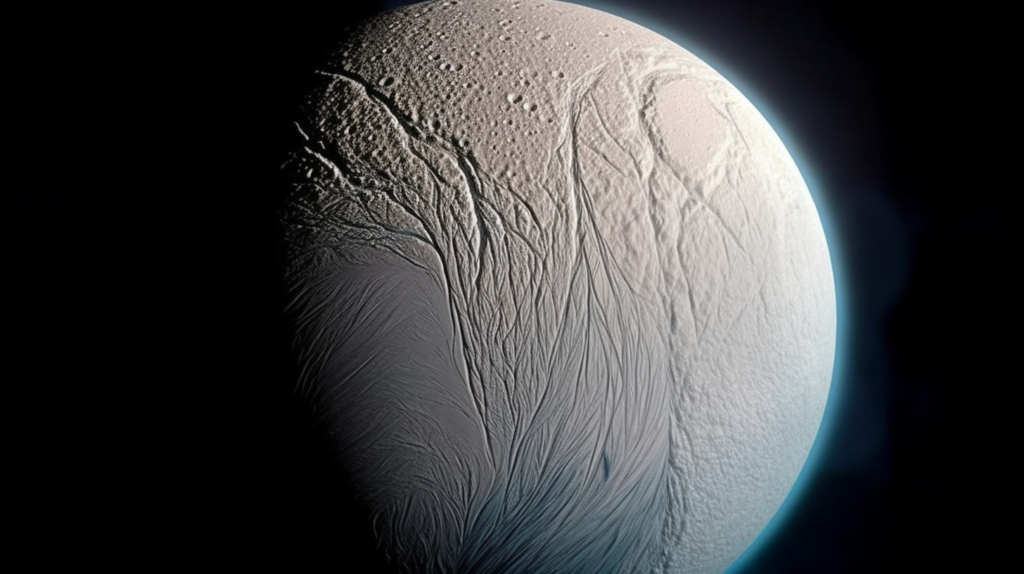
Enceladus: A Potential Abode for Life
Enceladus has all the right ingredients for life, with the recent discovery of phosphorus being the final piece of the puzzle. All life on Earth depends on six essential elements: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorus. Until now, phosphorus was the only one researchers had never detected beyond Earth. Enceladus has all the right ingredients for life and this significantly raises the prospect of finding life in the solar system beyond Earth.
The Discovery of Phosphorus: The Final Ingredient
The samples that confirmed the presence of phosphorus came from one of Saturn’s rings, primarily containing water ice spewed from geyser-like volcanoes in the liquid ocean deep beneath the moon’s icy surface. Prior examination of these samples detected little to no phosphorous. However, research using a new geochemical model suggests phosphorous is abundant on Enceladus, with concentrations at least 100 times higher than in Earth’s oceans.

Beyond the CO2 Snowline: Other Habitable Worlds
The findings suggest that other worlds beyond the CO2 snowline – the point in the outer solar system beyond which the sun’s rays no longer melt carbon dioxide, and it freezes into ice – could be as habitable as Enceladus. These include Pluto and Neptune’s moon Triton. Despite being too far from the sun to receive sufficient sunlight, these environments could support life. The essential heat could come from hydrothermal vents, which are abundant in Earth’s deepest oceans.
“Saturn’s sixth-largest moon, Enceladus has all the right ingredients for life, according to a new analysis of NASA’s Cassini space mission data. This discovery suggests that other similar moons in the outer solar system could also be habitable. The samples that confirmed the presence of phosphorus, the final piece of the puzzle, came from one of Saturn’s rings.“
“These samples primarily contain water ice spewed from geyser-like volcanoes in the liquid ocean deep beneath the moon’s icy surface. The findings suggest that other worlds beyond the CO2 snowline, including Pluto and Neptune’s moon Triton, could be as habitable as Enceladus. NASA recently detected a massive water eruption from Enceladus using the James Webb Telescope, which will likely uncover more information about this intriguing moon. The discovery of phosphorous on Enceladus, combined with the presence of the other five essential life elements, brings us one step closer to finding life beyond Earth.“
The Future of Exploration: Uncovering More About Enceladus
NASA detected a massive water eruption from Enceladus using the James Webb Telescope late last month. The plume spread over 6,000 miles – around 20 times the moon’s diameter. Further observations from the telescope will likely uncover more information about Enceladus, which has all the right ingredients for life.
Conclusion: Enceladus and the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The recent discovery of phosphorous on Enceladus, combined with the presence of the other five essential life elements, has brought us one step closer to finding life beyond Earth. As we continue to explore Enceladus and other celestial bodies, we can expect to gain more insights into the potential for life in our solar system and beyond. The fact that Enceladus has all the right ingredients for life serves as a reminder of the vast possibilities that space exploration holds.
Reference(s): Research Article






