The advancement of our species could be a captivating and complicated subject. Researchers frequently examine our long-gone relatives, the Neanderthals, and a few considers endeavor to unwind the truth approximately the captivating Denisovans. There are too other ground-breaking revelations that can shed more light on the advancement of people.
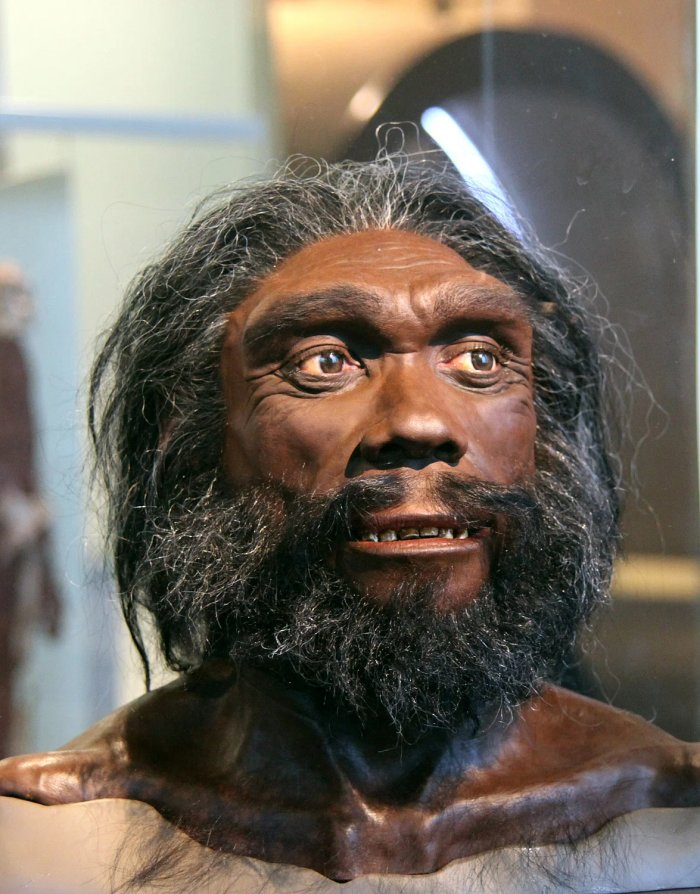

One such finding occurred in 1908 when fossils of an bygone human were found by a worker within the Rösch sandpit fair north of the town of Mauer, close Heidelberg, Germany. Researcher Otto Schoentensack, who was the primary one to look at and depict the fossil came up with the title Homo heidelbergensis.
Who Was Homo Heidelbergensis?
Nowadays, the fossil of Homo heidelbergensis is recognized as one of the classical finds of paleoanthropology. Homo heidelbergensis lived in Europe, conceivably Asia (China); Africa (eastern and southern). Researchers have long proposed Homo heidelbergensis who knew how to control fire by building hearths or early chimneys and utilize of wooden lances, lived almost 700,000 to 200,000 a long time prior.
“Why did they come together at these early hearths? Maybe to socialize, to discover consolation and warmth, to share nourishment and data, and to discover security from predators.
H. heidelbergensis likely took advantage of common covers but this species was moreover the primary to construct straightforward covers.”
Other archeological disclosures propose Homo heidelbergensis locked in in ceremonies, and these old people were able of creating instruments such a for illustration a handaxe.
Concurring to the Smithsonian’s National Exhibition hall of Normal History, “this species may reach back to 1.3 million a long time prior, and incorporate early people from Spain (‘Homo antecessor’ fossils and archeological evidence from 800,000 to 1.3 million a long time ancient), Britain (archeological remains back to approximately 1 million a long time ancient), and Italy (from the location of Ceprano, conceivably as ancient as 1 million a long time).
Comparison of Neanderthal and modern human DNA proposes that the two ancestries wandered from a common predecessor, most likely Homo heidelbergensis, at some point between 350,000 and 400,000 a long time prior – with the European department driving to H. neanderthalensis and the African department (now and then called Homo rhodesiensis) to H. sapiens.”
There’s no question that Homo heidelbergensis played an important portion in the history of human advancement. Still, the revelation of an antiquated cranium given researchers with interesting questions driving to unused hypotheses around the species.
Enigma Of The Broken Slope Cranium
Found in 1921 by mineworkers in what is presently Kabwe, Zambia, the Broken Slope (Kabwe 1) cranium is one of the best-preserved fossils of the early human species Homo heidelbergensis and was assessed to be approximately 500,000 a long time ancient. At the time of the disclosure, the Broken Slope remains were troublesome to date due to their indiscriminate recuperation and the location being totally annihilated by quarrying.
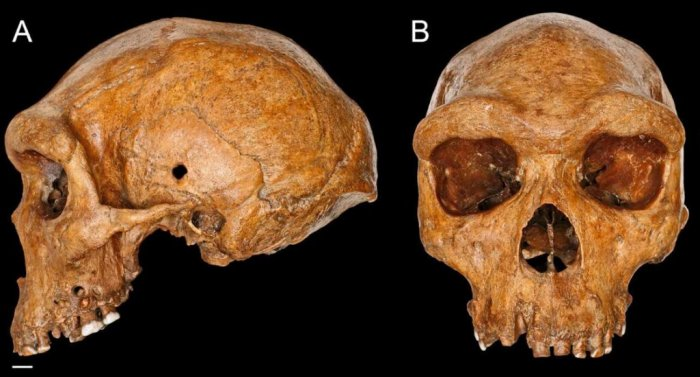
Characteristic History Museum London.
A few a long time prior, Teacher Rainer Grün from the Natural Prospects Inquire about Established driven the group which analyzed the cranium and other fossil human remains found within the region, counting a tibia and femur midshaft part. The comes about of the study driven to a ground-breaking revelation.
Utilizing radiometric dating methods, Teacher Grün and his colleagues evaluated the Broken Slope cranium is between 274,000 and 324,000 a long time ancient. It is much more youthful than already thought.
So, why is the dating of such significance, a few will inquire?
Concurring to Teacher Grün “the modern best age gauge of the fossil impacts our understanding of the tempo and mode of cutting edge human roots.”
The investigate moreover proposes that human advancement in Africa around 300,000 a long time prior was a much more complex prepare, with the co-existence of distinctive human ancestries.
“Already, the Broken Slope cranium was seen as portion of a slow and broad developmental grouping in Africa from age-old people to advanced people. But presently it looks just like the primitive species Homo naledi survived in southern Africa, H. heidelbergensis was in Central Africa, and early shapes of our species existed in districts like Morocco and Ethiopia,” Teacher Grün said.
Teacher Grün said his team’s research adds to modern and developing thinks about which address the mode of present day human advancement in Africa and whether Homo heidelbergensis is a coordinate precursor of our species.
Teacher Chris Stringer, a analyst in human advancement at the Characteristic History Exhibition hall, has worked with geochronologist Rainer Grün and other colleagues to deliver the leading assess for when the proprietor of the Broken Slope cranium passed on said the Broken Slope cranium is shockingly youthful.
“We as of now knew that Eurasia contained different human heredities almost 300,000 a long time ago. Now, the same applies to Africa, since H. heidelbergensis must have been modern with more sapiens-like fossils in Morocco and Kenya and the much more primitive Homo naledi, as of late found in South Africa.
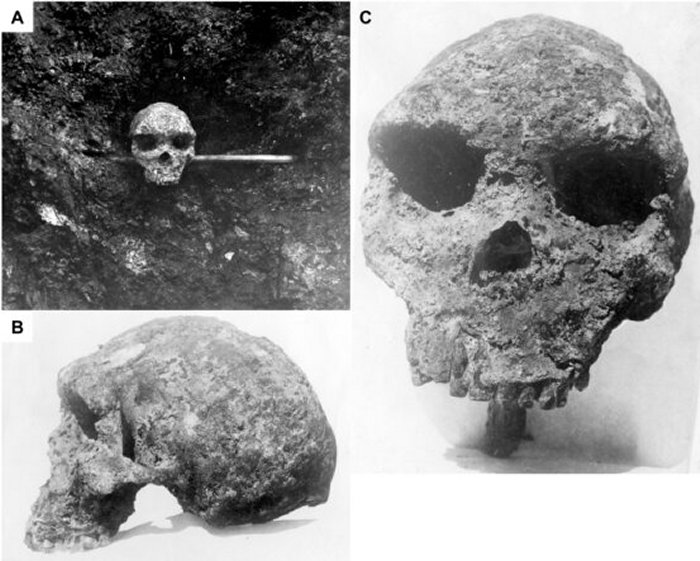
A date of almost 300,000 years old highlights the complexity of human advancement in Africa,” Professor Stringer clarified.
“It is presently looking like Africa and Eurasia were possessed by a entirety run of hominin species fair some hundred thousand a long time ago. While H. naledi was living in South Africa, H. heidelbergensis was surviving in South-Central Africa, and H. sapiens was developing in Morocco and Ethiopia.
At the same time as all this H. neanderthalensis was advancing in Europe, the Denisovans were creating in Asia, Homo erectus may still have been clinging on in Indonesia, and two little hominins, Homo floresiensis and Homo luzonensis, were living the island life in Southeast Asia.
It appears that the world was a active put, and we’re as it were now starting to get it what this may cruel for our possess roots.”
Composed by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Essayist






